The Cornerstone Professional Group, LLC
Business and IT Consulting
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Do you know the terminology? Backups may not be the only thing you need. We have it down to a science. We’ll work with you to determine the types of data and applications you use, their criticality, and your risk tolerance. Based on your budget, we will design a Business Continuity strategy that fits your situation. Get your tech on and review the information below:
High Availability
High Availability or “HA”, is a business continuity strategy to keep systems available in the event of a system failure by running a parallel instance of the application/data in question. For instance, Office 365, specifically Exchange online, is an example of an HA application where Microsoft runs multiple Exchange servers in their datacenters with multiple copies of the Exchange/Email data.
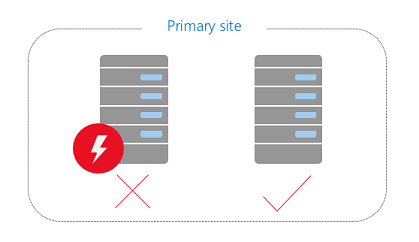
Scenario: If there is a hardware or network issue with one of the Exchange servers, the HA instance steps in quickly to service the email in a manner that is invisible to the users. The primary Exchange server can then be repaired offline and later, the services failed back to the primary server if required. This is how Microsoft can offer a 99.9% SLA for Exchange services.
What HA is NOT: HA is not a backup solution. If there is data corruption, deletion or data loss, having HA does NOT allow you to recover that data. You basically have multiple copies of bad data. Not helpful.
RPO and RTO
Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The target point in time prior to a disruptive event to which data can be recovered
Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum target duration after a disruptive event occurs which will elapse before IT services are restored
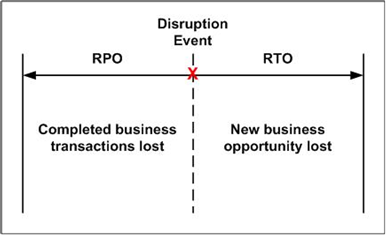
Generally the tighter the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), the more expensive the solution.
Backup and Retention
Backup: A copy of your data at a point in time.
Retention: How many backups you will keep, and how far back they may go.
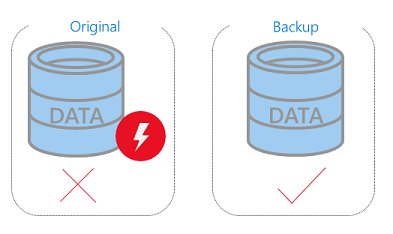
When your data is corrupted, deleted, or lost you can restore it.
Scenario: A user deletes a file or email and does not realize it until weeks later. Backups provide the ability to find and restore the data.
What backup is NOT: Backup is not a quick recovery solution. It just means you have another copy of your data from some point in time. Recovering from backup could possibly take days/weeks depending on the backup methodology that is in place, and the type of disruption that occurred.
Backup parameters should be determined ahead of time – what gets backed up and its frequency. Retention should also be determined ahead of time. An example retention policy may be to store daily backups for 14 days, weekly backups for 4 weeks, monthly backups for 12 months, and yearly backups for 7 years.
With this type of back up and retention, you should be able to go back to any recovery point in your retention policy to find data you need to restore.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster Recovery: The ability to bring systems and data online after a catastrophic failure or loss at the primary service site.
Scenario: A natural disaster destroys the site where your primary IT infrastructure is located, rendering IT services inoperable. The Disaster Recovery (DR) plan would be initiated to bring systems back online at another location within the target RPO and RTO.
What Disaster Recovery is NOT: Disaster Recovery is NOT a backup solution. Only the most recent copy of data is stored in the DR site to allow for rapid spin up. You typically cannot retrieve data from weeks/months ago with a DR solution.
There are various strategies for disaster recovery, each is suitable depending on the business need or RPO/RTO. Some RPO/RTO can approach 1-2 hours, while others may be days. Depending on your business requirement, risk tolerance, and target budget, we can design a solution that will work for you.
Interested and want to know more?
Contact Us